Appearance
生成曲线、几何体
生成圆弧顶点
绘制圆弧本质是绘制一个正 n 边形, n 越多, 圆弧越光滑精度越高
指定圆弧半径, 相邻点间隔弧度, 分段数量
jsconst R = 100; //圆弧半径 const N = 50; //分段数量 const sp = (2 * Math.PI) / N; //两个相邻点间隔弧度生成圆弧顶点数据
js// 批量生成圆弧上的顶点数据 const arr = []; // N控制圆弧精度:就是创建多少个顶点 for (let i = 0; i < N; i++) { const angle = sp * i; //当前点弧度 // 以坐标原点为中心,在XOY平面上生成圆弧上的顶点数据 const x = R * Math.cos(angle); const y = R * Math.sin(angle); arr.push(x, y, 0); //xyz坐标 }用线模型渲染出圆弧线
js// 线材质 const material = new THREE.LineBasicMaterial({ color: 0xff0000, //线条颜色 }); // 创建线模型对象 构造函数:Line、LineLoop、LineSegments // const line = new THREE.Line(geometry, material); const line = new THREE.LineLoop(geometry, material); //封闭缺口
几何体方法.setFromPoints()
可以把声明的顶点坐标里面坐标数据提取出来,赋值给 geometry.attributes.position 属性
三维向量
jsconst pointsArr = [ // 三维向量Vector3表示的坐标值 new THREE.Vector3(0, 0, 0), new THREE.Vector3(0, 100, 0), new THREE.Vector3(0, 100, 100), new THREE.Vector3(0, 0, 100), ]; // 把数组pointsArr里面的坐标数据提取出来 // 赋值给`geometry.attributes.position`属性 geometry.setFromPoints(pointsArr); console.log("几何体变化", geometry.attributes.position);二维向量
jsconst pointsArr = [ // 三维向量Vector2表示的坐标值 new THREE.Vector2(0, 0), new THREE.Vector2(100, 0), new THREE.Vector2(100, 100), new THREE.Vector2(0, 100), ]; geometry.setFromPoints(pointsArr);
曲线curve
three.js 提供了很多常用的曲线或直线 API,可以直接使用。它们的共同父类是curve
.getPoints()
可以从曲线上获取顶点数据, 细分数越高返回的顶点数量越多,自然轮廓越接近于曲线形状。返回值是一个由二维向量 Vector2 或三维向量 Vector3 构成的数组js//平面曲线会返回一个vector2对象作为元素组成的数组 const pointsArr = arc.getPoints(50); //分段数50,返回51个顶点 console.log("曲线上获取坐标", pointsArr);.getSpacedPoints()
和.getPoints()类似,不同在于.getSpacedPoints()按照曲线长度等间距返回顶点数据,.getPoints()会考虑曲线斜率变化,斜率变化快的位置返回的顶点更密集
椭圆和圆
椭圆弧线EllipseCurve
js
EllipseCurve(aX, aY, xRadius, yRadius, aStartAngle, aEndAngle, aClockwise);| 参数 | 含义 |
|---|---|
| aX, aY | 中心坐标 |
| xRadius | x 轴半径 |
| yRadius | y 轴半径 |
| aStartAngle | 弧线开始角度,从 x 轴正半轴开始,默认 0 |
| aEndAngle | 弧线结束角度,从 x 轴正半轴算起,默认 2 x Math.PI |
| aClockwise | 是否顺时针绘制,默认值为 false |
圆弧线ArcCurve
js
ArcCurve(aX, aY, aRadius, aStartAngle, aEndAngle, aClockwise);| 参数 | 含义 |
|---|---|
| aX, aY | 中心坐标 |
| aRadius | 圆弧半径 |
| aStartAngle | 弧线开始角度,从 x 轴正半轴开始,默认 0 |
| aEndAngle | 弧线结束角度,从 x 轴正半轴算起,默认 2 x Math.PI |
| aClockwise | 是否顺时针绘制,默认值为 false |
样条曲线
通过一系列点创建平滑的样条曲线
三维样条曲线CatmullRomCurve3
创建一组三维 Vector3 顶点坐标
jsconst arr = [ new THREE.Vector3(-50, 20, 90), new THREE.Vector3(-10, 40, 40), new THREE.Vector3(0, 0, 0), new THREE.Vector3(60, -60, 0), new THREE.Vector3(70, 0, 80), ]; // 三维样条曲线 const curve = new THREE.CatmullRomCurve3(arr);从曲线获取顶点坐标,绘制线条
js//曲线上获取点 const pointsArr = curve.getPoints(100); const geometry = new THREE.BufferGeometry(); //读取坐标数据赋值给几何体顶点 geometry.setFromPoints(pointsArr); // 线材质 const material = new THREE.LineBasicMaterial({ color: 0x00fffff, }); // 线模型 const line = new THREE.Line(geometry, material);可视化曲线经过点坐标
js//... const material2 = new THREE.PointsMaterial({ color: 0xff00ff, size: 10, }); //点模型对象 const points = new THREE.Points(geometry2, material2);
2D 样条曲线SplineCurve
默认在 XOY 平面生成一个平面的样条曲线, 参数是二维向量对象 Vector2 构成的数组
js
// 二维向量Vector2创建一组顶点坐标
const arr = [new THREE.Vector2(-100, 0), new THREE.Vector2(0, 30), new THREE.Vector2(100, 0)];
// 二维样条曲线
const curve = new THREE.SplineCurve(arr);贝塞尔曲线
二维二次贝塞尔曲线QuadraticBezierCurve
js
// p1、p3是曲线起始点,p2是曲线的控制点
const p1 = new THREE.Vector2(-80, 0);
const p2 = new THREE.Vector2(20, 100);
const p3 = new THREE.Vector2(80, 0);
const curve = new THREE.QuadraticBezierCurve(p1, p2, p3);
//读取点位坐标, 创建线模型渲染
//...三维二次贝塞尔曲线QuadraticBezierCurve3
js
// p1、p2、p3表示三个点坐标
const p1 = new THREE.Vector3(-80, 0, 0);
const p2 = new THREE.Vector3(20, 100, 0);
const p3 = new THREE.Vector3(80, 0, 100);
const curve = new THREE.QuadraticBezierCurve3(p1, p2, p3);
//...二维三次贝塞尔曲线CubicBezierCurve
区别二次多了一个控制点
js
// p1、p4是曲线起始点,p2、p3是曲线的控制点
const p1 = new THREE.Vector2(-80, 0);
const p2 = new THREE.Vector2(-40, 50);
const p3 = new THREE.Vector2(50, 50);
const p4 = new THREE.Vector2(80, 0);
// 二维三次贝赛尔曲线
const curve = new THREE.CubicBezierCurve(p1, p2, p3, p4);三维三次贝塞尔曲线CubicBezierCurve3
js
const p1 = new THREE.Vector3(-80, 0, 0);
const p2 = new THREE.Vector3(-40, 50, 0);
const p3 = new THREE.Vector3(50, 50, 0);
const p4 = new THREE.Vector3(80, 0, 100);
// 三维三次贝赛尔曲线
const curve = new THREE.CubicBezierCurve3(p1, p2, p3, p4);组合曲线CurvePath
可以将直线、圆弧、贝塞尔曲线拼接成一条曲线, 要注意拼接顺序
js
const R = 100;
const H = 200;
// 创建弧线
const arc = new THREE.ArcCurve(0, 0, R, 0, Math.PI, true);
// 创建两条直线
const line1 = new THREE.LineCurve(new THREE.Vector2(R, H), new THREE.Vector2(R, 0));
const line2 = new THREE.LineCurve(new THREE.Vector2(-R, 0), new THREE.Vector2(-R, H));
// 创建组合曲线对象
const curvePath = new THREE.CurvePath();
// 拼接出来一个U型轮廓曲线,注意顺序
curvePath.curves.push(line1, arc, line2);曲线路径管道TubeGeometry
基于一个 3D 曲线路径,生成一个管道几何体
js
TubeGeometry(path, tubularSegments, radius, radiusSegments, closed);| 参数 | 值 |
|---|---|
| path | 扫描路径,路径要用三维曲线 |
| tubularSegments | 路径方向细分数,默认 64 |
| radius | 管道半径,默认 1 |
| radiusSegments | 管道圆弧细分数,默认 8 |
| closed | Boolean 值,管道是否闭合 |
创建管道
js
// 三维样条曲线
const path = new THREE.CatmullRomCurve3([
new THREE.Vector3(-50, 20, 90),
new THREE.Vector3(-10, 40, 40),
new THREE.Vector3(0, 0, 0),
new THREE.Vector3(60, -60, 0),
new THREE.Vector3(70, 0, 80),
]);
// path:路径 40:沿着轨迹细分数 2:管道半径 25:管道截面圆细分数
const geometry = new THREE.TubeGeometry(path, 40, 2, 25);其它贝塞尔曲线、拼接曲线等三维曲线都可以作为管道路径
观察管道内壁
threejs 默认只渲染 mesh 三角形的正面,如果想看到管道内壁,可以设置双面渲染THREE.DoubleSide
js
const material = new THREE.MeshLambertMaterial({
side: THREE.DoubleSide, //双面显示看到管道内壁
});旋转成型LatheGeometry
利用一个 2D 轮廓,经过旋转变换生成一个 3D 的几何体曲面 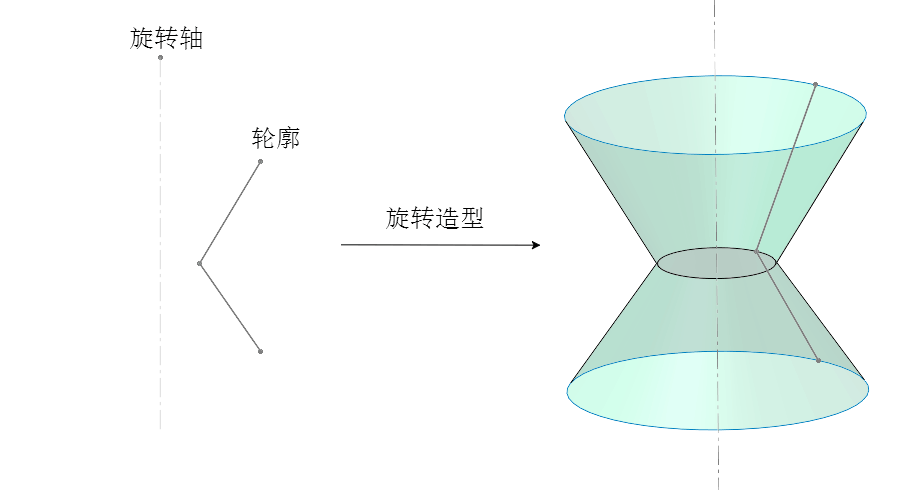
js
LatheGeometry(points, segments, phiStart, phiLength);| 参数 | 值 |
|---|---|
| points | Vector2 坐标数据组成的轮廓数组 |
| segments | 圆周方向细分数,默认 12 |
| phiStart | 开始角度,默认 0 |
| phiLength | 旋转角度,默认 2π |
直线轮廓
js
// Vector2表示的三个点坐标,三个点构成的轮廓相当于两端直线相连接
const pointsArr = [new THREE.Vector2(50, 60), new THREE.Vector2(25, 0), new THREE.Vector2(50, -60)];
// LatheGeometry:pointsArr轮廓绕y轴旋转生成几何体曲面
// pointsArr:旋转几何体的旋转轮廓形状
const geometry = new THREE.LatheGeometry(pointsArr);曲线生成轮廓
js
// 通过三个点定义一个二维样条曲线
const curve = new THREE.SplineCurve([
new THREE.Vector2(50, 60),
new THREE.Vector2(25, 0),
new THREE.Vector2(50, -60),
]);
//曲线上获取点,作为旋转几何体的旋转轮廓
const pointsArr = curve.getPoints(50);
// LatheGeometry:pointsArr轮廓绕y轴旋转生成几何体曲面
const geometry = new THREE.LatheGeometry(pointsArr, 30);轮廓填充ShapeGeometry
通过一个多边形外轮廓坐标生成一个多边形几何体平面
1.多边形轮廓shape
坐标要按照顺序依次排列
js
// 一组二维向量表示一个多边形轮廓坐标
const pointsArr = [
new THREE.Vector2(-50, -50),
new THREE.Vector2(-60, 0),
new THREE.Vector2(0, 50),
new THREE.Vector2(60, 0),
new THREE.Vector2(50, -50),
];
// Shape表示一个平面多边形轮廓,参数是二维向量构成的数组pointsArr
const shape = new THREE.Shape(pointsArr);2.轮廓填充几何体ShapeGeometry
把五边形轮廓Shape作为ShapeGeometry的参数,形成一个多边形平面几何体。
js
const geometry = new THREE.ShapeGeometry(shape);3.查看ShapeGeometry生成的三角形
平面几何体本质是三角型拼接而成, 通过设置wireframe可以查看
js
const material = new THREE.MeshLambertMaterial({
wireframe: true,
});拉伸ExtrudeGeometry
基于一个基础的平面轮廓Shape进行变换,生成一个几何体 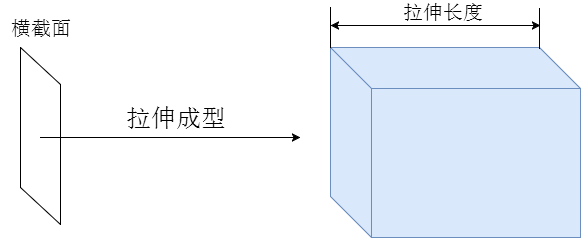
1. 定义一个shape轮廓
js
// Shape表示一个平面多边形轮廓
const shape = new THREE.Shape([
// 按照特定顺序,依次书写多边形顶点坐标
new THREE.Vector2(-50, -50), /
new THREE.Vector2(-50, 50),
new THREE.Vector2(50, 50),
new THREE.Vector2(50, -50),
]);2. 拉伸成型
js
//拉伸造型
const geometry = new THREE.ExtrudeGeometry(
shape, //二维轮廓
{
depth: 20, //拉伸长度
}
);3. 拉伸倒角
- 倒圆角
js
const geometry = new THREE.ExtrudeGeometry(shape, {
depth: 20,
bevelThickness: 5, //倒角尺寸:拉伸方向
bevelSize: 5, //倒角尺寸:垂直拉伸方向
bevelSegments: 20, //倒圆角:倒角细分精度,默认3
});- 倒直角
js
const geometry = new THREE.ExtrudeGeometry(shape, {
bevelSegments: 1, //倒直角
});- 取消默认倒角
js
//拉伸造型
const geometry = new THREE.ExtrudeGeometry(
shape, //二维轮廓
{
depth: 20, //拉伸长度
bevelEnabled: false, //禁止倒角,默认true
}
);扫描ExtrudeGeometry
基于一个基础的平面轮廓Shape,沿着曲线扫描成型 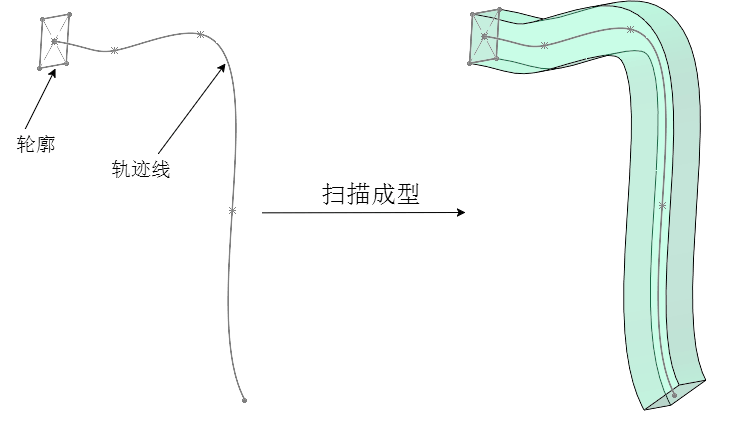
1. 扫描轮廓
js
// 扫描轮廓:Shape表示一个平面多边形轮廓
const shape = new THREE.Shape([
// 按照特定顺序,依次书写多边形顶点坐标
new THREE.Vector2(0, 0), //多边形起点
new THREE.Vector2(0, 10),
new THREE.Vector2(10, 10),
new THREE.Vector2(10, 0),
]);2. 扫描路径
js
// 扫描轨迹:创建轮廓的扫描轨迹(3D样条曲线)
const curve = new THREE.CatmullRomCurve3([
new THREE.Vector3(-10, -50, -50),
new THREE.Vector3(10, 0, 0),
new THREE.Vector3(8, 50, 50),
new THREE.Vector3(-5, 0, 100),
]);3. 扫描造型
js
//扫描造型:扫描默认没有倒角
const geometry = new THREE.ExtrudeGeometry(
shape, //扫描轮廓
{
extrudePath: curve, //扫描轨迹
steps: 100, //沿着路径细分精度,越大越光滑
}
);多边形轮廓 Shape
Shape的父类是Path,Path提供了直线、圆弧、贝塞尔、样条等绘制方法,Shape也继承了这些方法
Shape基础方法
currentPoint: 当前点,默认值 Vector2(0,0)moveTo(): 移动到某一个坐标点, 会改变.currentPoint属性jsconst shape = new THREE.Shape(); shape.moveTo(10, 0);绘制直线
.lineTo(): 从当前点绘制一条直线到指定结束点; 同样会改变.currentPoint属性jsconst shape = new THREE.Shape(); shape.moveTo(10, 0); //.currentPoint变为(10,0) // 绘制直线线段,起点(10,0),结束点(100,0) shape.lineTo(100, 0);
绘制圆弧
圆弧
.arc下面代码绘制了一个矩形+扇形的轮廓,圆心在(100, 0),半径 50。
jsconst shape = new THREE.Shape(); shape.lineTo(100 + 50, 0); //.currentPoint变为(100+50,0) // 圆弧.arc参数的圆心0,0坐标是相对当前.currentPoint而言,而不是坐标原点 shape.arc(-50, 0, 50, 0, Math.PI / 2); //.currentPoint变为圆弧线结束点坐标 // 绘制直线,直线起点:圆弧绘制结束的点 直线结束点:(0, 0) shape.lineTo(0, 50);TIP
.arc圆心坐标是相对当前.currentPoint而言, 而不是坐标原点- 直线和圆弧起点之间的缺口 threejs 内部会自动补上
绝对圆弧
.absarc.absarc()圆心坐标不受到.currentPoint影响,以坐标原点作为参考jsconst shape = new THREE.Shape(); shape.lineTo(100, 0); //.currentPoint变为(100,0) // absarc圆心坐标不受到.currentPoint影响,以坐标原点作为参考 shape.absarc(100, 0, 50, 0, Math.PI / 2); //.currentPoint变为圆弧线结束点坐标 shape.lineTo(0, 50);shape作为几何体参数当
shape作为曲线轮廓被调用时, 可以通过设置分段数提高曲线光滑度js// shape:填充轮廓 const geometry = new THREE.ShapeGeometry(shape, 20);jsconst geometry = new THREE.ExtrudeGeometry(shape, { depth: 20, //拉伸长度 bevelEnabled: false, //禁止倒角 curveSegments: 20, //shape曲线对应曲线细分数 });
内孔
在平面多边形内部设置孔洞 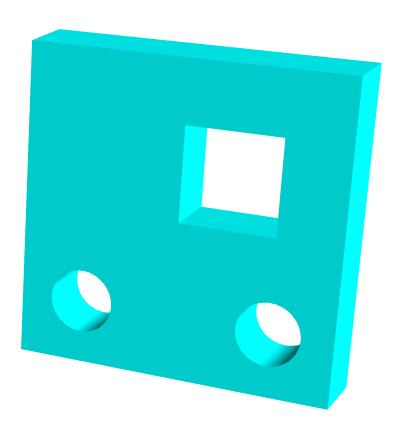
创建外部轮廓
jsconst shape = new THREE.Shape(); // .lineTo(100, 0)绘制直线线段,线段起点:.currentPoint,线段结束点:(100,0) shape.lineTo(100, 0); shape.lineTo(100, 100); shape.lineTo(0, 100);设置内孔轮廓
jsconst path1 = new THREE.Path(); // 圆孔1 path1.absarc(20, 20, 10); const path2 = new THREE.Path(); // 圆孔2 path2.absarc(80, 20, 10); const path3 = new THREE.Path(); // 方形孔 path3.moveTo(50, 50); path3.lineTo(80, 50); path3.lineTo(80, 80); path3.lineTo(50, 80); //三个内孔轮廓分别插入到holes属性中 shape.holes.push(path1, path2, path3);
模型边界线
创建 mesh 几何体
jsconst geometry = new THREE.BoxGeometry(50, 50, 50); const material = new THREE.MeshLambertMaterial({ color: 0x004444, transparent: true, opacity: 0.5, }); const mesh = new THREE.Mesh(geometry, material);用
EdgesGeometry重新计算, 创建一个新的几何体js// 长方体作为EdgesGeometry参数创建一个新的几何体 const edges = new THREE.EdgesGeometry(geometry); const edgesMaterial = new THREE.LineBasicMaterial({ color: 0x00ffff, });用线模型
LineSegments渲染新的几何体并添加jsconst line = new THREE.LineSegments(edges, edgesMaterial); mesh.add(line);
几何顶点颜色数据
1. 顶点颜色
- 顶点位置数据
geometry.attributes.position - 顶点颜色数据
geometry.attributes.color
顶点颜色数据和顶点位置数据一一对应
顶点位置数据
jsconst geometry = new THREE.BufferGeometry(); //创建一个几何体对象 const vertices = new Float32Array([0, 0, 0, 50, 0, 0, 0, 25, 0]); // 顶点位置 geometry.attributes.position = new THREE.BufferAttribute(vertices, 3);顶点颜色数据
jsconst colors = new Float32Array([1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0]); // 设置几何体attributes属性的颜色color属性 //3个为一组,表示一个顶点的颜色数据RGB geometry.attributes.color = new THREE.BufferAttribute(colors, 3);点渲染
js// 点渲染模式 const material = new THREE.PointsMaterial({ // color: 0x333333,//使用顶点颜色数据,color属性可以不用设置 vertexColors: true, //默认false,设置为true表示使用顶点颜色渲染 size: 20.0, //点对象像素尺寸 }); const points = new THREE.Points(geometry, material); //点模型对象
2. 颜色渐变
当用线模型渲染时, 直线颜色是渐变的状态
js
const material = new THREE.LineBasicMaterial({
vertexColors: true, //使用顶点颜色渲染
});
const line = new THREE.Line(geometry, material);3. 网格模型颜色渐变
当使用网格模型 mesh 渲染, 也会产生渐变效果
js
const material = new THREE.MeshBasicMaterial({
// color: 0x333333,//使用顶点颜色数据,color属性可以不用设置
vertexColors: true, //默认false,设置为true表示使用顶点颜色渲染
side: THREE.DoubleSide,
});
const mesh = new THREE.Mesh(geometry, material);4. 曲线颜色渐变
生成样条曲线
jsconst geometry = new THREE.BufferGeometry(); //创建一个几何体对象 const curve = new THREE.CatmullRomCurve3([ new THREE.Vector3(-50, 20, 90), new THREE.Vector3(-10, 40, 40), new THREE.Vector3(0, 0, 0), new THREE.Vector3(60, -60, 0), new THREE.Vector3(70, 0, 80), ]); const pointsArr = curve.getSpacedPoints(100); //曲线取点 geometry.setFromPoints(pointsArr); //pointsArr赋值给顶点位置属性通过循环逐一给顶点赋 color 值
jsconst pos = geometry.attributes.position; const count = pos.count; //顶点数量 // 计算每个顶点的颜色值 const colorsArr = []; for (let i = 0; i < count; i++) { const percent = i / count; //点索引值相对所有点数量的百分比 //根据顶点位置顺序大小设置颜色渐变 // 红色分量从0到1变化,蓝色分量从1到0变化 colorsArr.push(percent, 0, 1 - percent); //蓝色到红色渐变色 } //类型数组创建顶点颜色color数据 const colors = new Float32Array(colorsArr); // 设置几何体attributes属性的颜色color属性 geometry.attributes.color = new THREE.BufferAttribute(colors, 3);线模型渲染渐变色曲线
jsconst material = new THREE.LineBasicMaterial({ vertexColors: true, //使用顶点颜色渲染 }); const line = new THREE.Line(geometry, material);
Color 颜色渐变插值
颜色插值方法.lerpColors()
js
.lerpColors(Color1,Color2, percent)通过一个百分比参数percent, 控制 Color1 和 Color2 两种颜色混合的百分比; Color1 对应 1-percent,Color2 对应 percent
js
const c1 = new THREE.Color(0xff0000); //红色
const c2 = new THREE.Color(0x0000ff); //蓝色
const c = new THREE.Color();
c.lerpColors(c1, c2, 0.5);颜色插值方法.lerp()
c1 与 c2 颜色混合,混合后的 rgb 值,赋值给 c1 的.r、.g、.b 属性。
js
const c1 = new THREE.Color(0xff0000); //红色
const c2 = new THREE.Color(0x0000ff); //蓝色
c1.lerp(c2, percent);注意
混合后会改变 c1 的颜色
颜色克隆.clone
通过克隆返回一个新的颜色对象, 不会修改原有颜色属性
js
const c1 = new THREE.Color(0xff0000); //红色
const c2 = new THREE.Color(0x0000ff); //蓝色
const c = c1.clone().lerp(c2, percent); //颜色插值计算差值应用
给曲线顶点赋 color 值生成渐变
js
//...
const c1 = new THREE.Color(0x00ffff); //曲线起点颜色 青色
const c2 = new THREE.Color(0xffff00); //曲线结束点颜色 黄色
for (let i = 0; i < count; i++) {
const percent = i / count; //点索引值相对所有点数量的百分比
//根据顶点位置顺序大小设置颜色渐变
const c = c1.clone().lerp(c2, percent); //颜色插值计算
colorsArr.push(c.r, c.g, c.b);
}查看或设置 gltf 几何体顶点
获取 gltf 模型几何体顶点数据
js
loader.load("../地形.glb", function (gltf) {
model.add(gltf.scene); //三维场景添加到model组对象中
//mesh表示地形网格模型
const mesh = gltf.scene.children[0];
// 顶点数据
const att = mesh.geometry.attributes;
// 顶点位置数据
const pos = mesh.geometry.attributes.position;
const count = pos.count; //几何体顶点数量
});几何体顶点索引属性geometry.index
three.js 大部分自带的几何体 API 默认有.index 属性,外部加载的 gltf 等模型,geometry.index 数据可能有,也可能没有
js
console.log("index", mesh.geometry.index);读取顶点坐标数据.getX()、.getY()和.getZ()
js
const pos = mesh.geometry.attributes.position;
// 获取几何体第一个顶点的x坐标
const x = pos.getX(0);修改顶点坐标数据.setX()、.setY()和.setZ()
js
const pos = mesh.geometry.attributes.position;
pos.setX(0, 100);